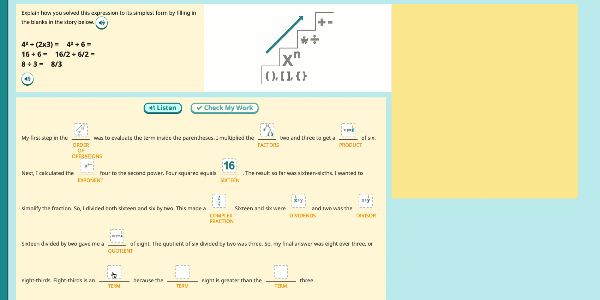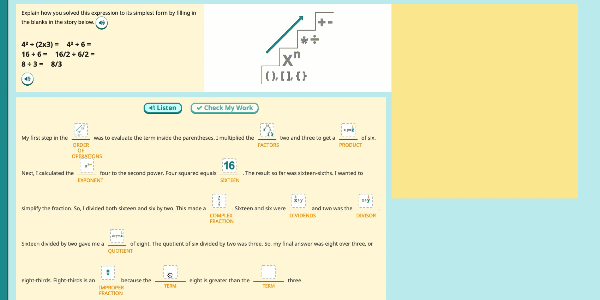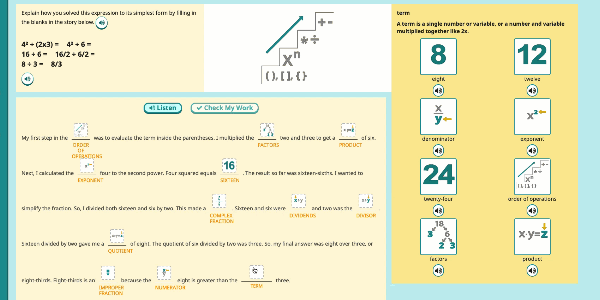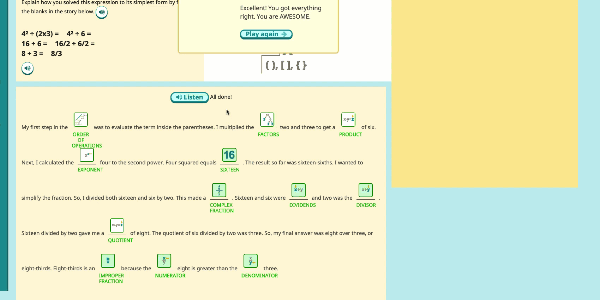
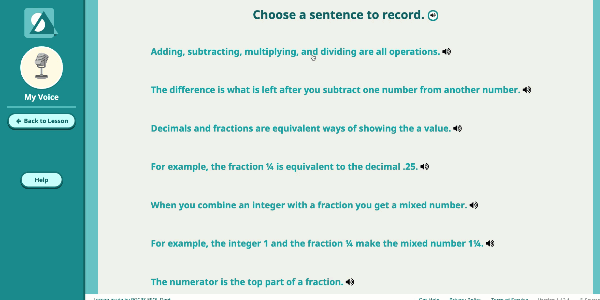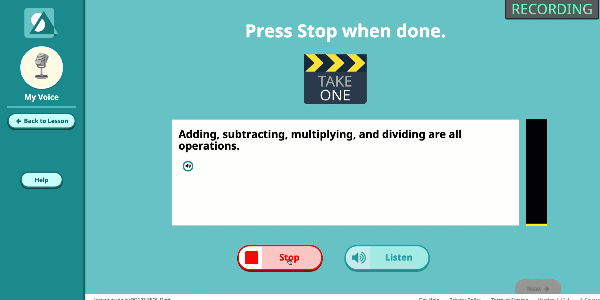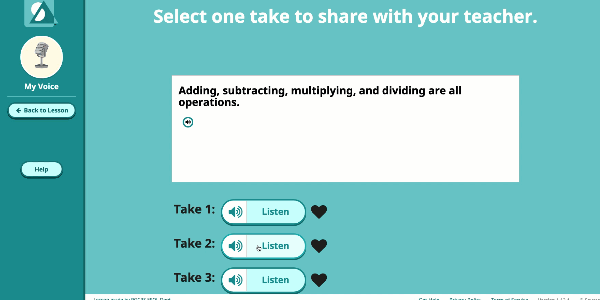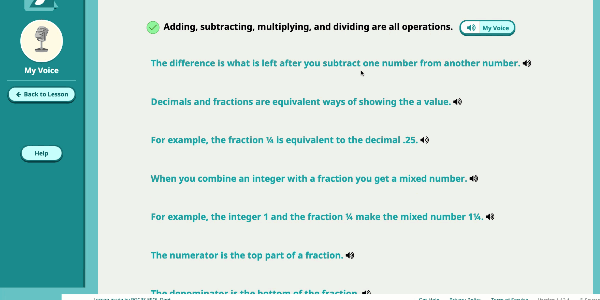
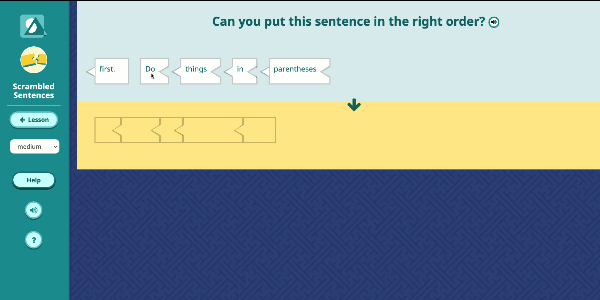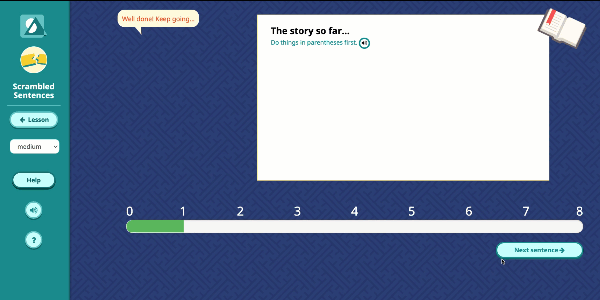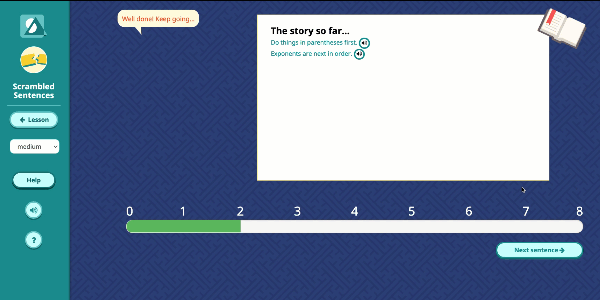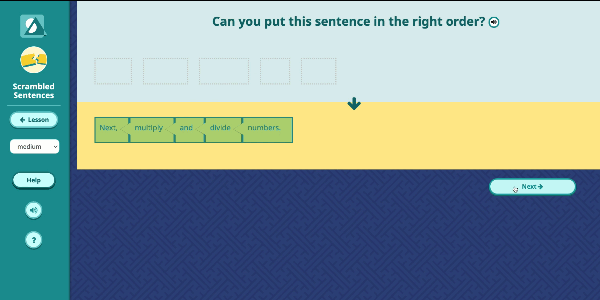
Speak Agent’s High School Math program significantly improves outcomes by developing conceptual understanding of advanced math concepts, as well as reasoning, modeling, and mathematical discourse. How? By seamlessly integrating academic language activities, real-world math stories, reading and writing scaffolds, tools for high school students to create and share word problems, and many other research-based Math+Language strategies.
Math Courses Available for High School
Algebra 1
Speak Agent Algebra+Language℠ helps students to master key Algebra 1 concepts and to develop critical skills such as math communication, algebraic thinking, and problem-solving.
| Unit | Common Core State Standards |
|---|---|
| Characteristics of Linear Functions | F.LE.2, F.IF.3 |
| Functions and Function Notation | F.IF.1, F.IF.2 |
| Graphing Linear Functions | F.IF.6, F.LE.1a, F.LE.1b, A.CED.2, A.REI.10, F.BF.1, F.BF.1a, F.IF.4, F.IF.5, F.IF.7a, F.LE.1a, F.LE.1b, F.LE.2, F.LE.5 |
| Applications of Linear Functions | S.ID.6, S.ID.6a, S.ID.6c, S.ID.7, F.BF.3 |
| Linear Equations and Inequalities | A.SSE.1a, A.SSE.1b, A.SSE.2, A.CED.1, A.CED.3, A.CED.4, A.REI.1, A.REI.3 |
| Systems of Linear Equations | A.REI.5, A.REI.6, A.REI.11, A.REI.12, A.CED.3 |
| Quadratic Functions | A.APR.3, A.CED.2, A.REI.10, F.BF.1, F.BF.1a, F.BF.3, F.IF.2, F.IF.4, F.IF.5, F.IF.6, F.IF.7a, F.IF.8a |
| Rational and Irrational Number Operations | N.RN.3 |
| Solving Quadratic Functions | A.APR.1, A.SSE.1a, A.SSE.1b, A.SSE.2, A.SSE.3a, A.SSE.3b |
| Using Quadratic Equations to Solve Problems | A.CED.1, A.CED.4, A.REI.1, A.REI.4a, A.REI.4b |
| Introducing Exponential Functions | A.CED.2, F.BF.1, F.BF.1a, F.IF.2, F.IF.3, F.IF.4, F.IF.5, F.LE.1a, F.LE.1c, F.LE.2, F.LE.5, F.IF.6, F.LE.1a, F.LE.1c, A.SSE.1a, A.SSE.1b, A.SSE.2, A.SSE3c |
| Exponential Equations | A.CED.1, F.IF.2 |
| Bivariate Data and Analyzing Fit | S.ID.6, S.ID.6a, S.ID.6b, S.ID.8, S.ID.9 |
| Characteristics of Functions | F.LE.3, F.IF.9 |
| Systems of Equations | A.REI.11 |
| Types of Functions | F.IF.2, F.IF.4, F.IF.5, F.IF.7b |
Algebra 2
| Unit | Common Core State Standards |
|---|---|
| Quadratic Functions | F.BF.1, F.BF.1a, F.LE.2, F.LE.5 |
| Solving Quadratic Functions | N.CN.1, N.CN.2 A.SSE.2, N.CN.7, A,CED.1, A.REI.1, A.REI.4b, A.REI.7, A.REI.11 |
| Inverse Functions | F.BF.4a |
| Radical Functions | N.RN.1, N.RN.2, A.REI.1, A.REI.2 |
| Polynomial Division, Factors, and Zeros | A.APR.2, A.APR.4, A.APR.6, A.SSE.2 |
| Rational Functions | A.CED.1, A.REI.1, A.REI.2 |
| Polynomial Functions | A.APR.3, F.BF.1, F.IF.4, F.IF.6, F.IF.7c |
| Characteristics of Polynomial Functions | F.BF.3 |
| Introducing Exponential Functions | F.BF.1, F.BF.1a, F.IF.4, F.IF.6, F.IF.7e, F.LE.2 |
| Exponential Functions and Expressions | A.SSE.2, A.SSE.3c, F.BF.1, F.BF.3, F.IF.8b |
| Sequences and Series | A.SSE.4, F.BF.2 |
| Exponential Equations | A.SSE.2, A.CED.1, A.REI.1, F.LE.4 |
| Logarithmic Function | F.IF.4, F.IF.6, F.IF.7e |
| Rules of Logarithms | F.BF.3 |
| Unit Circle | F.TF.1, F.TF.2 |
| Graphing Trigonometric Functions | F.BF.1, F.BF.3, F.IF.4, F.IF.6, F.IF.7e |
| Modeling Bivariate Data & Periodic Phenomena | F.TF.5, S.ID.6a |
| Combining Functions with Arithmetic Operations | F.BF.1b |
| Comparing Properties of Functions | F.IF.9 |
| Solving Equations and Simultaneous Equations Using Intersection Points | A.REI.11 |
Applications in Algebra (sheltered Algebra prep course for newcomer ELs)
| Unit | Key Learning Objectives | CCSS Standards |
|---|---|---|
| Transitional Unit | ||
| Unit 00A: Whole Numbers, Place Value, Fractions | Written numbers. Labeling place values and decimal operations. Relationships among fractions Decimals and percentages. | (Prior-year review.) |
| Unit 00B: Ratios & Conversion | Converting fractions and decimals. Equivalent fractions. Relationships among fractions, percentages, and ratios. | (Prior-year review.) |
| Unit 00C: Perimeter & Area of 2D Shapes | Finding the perimeter. Finding the area. | (Prior-year review.) |
| Unit 1: Equivalent Expressions | ||
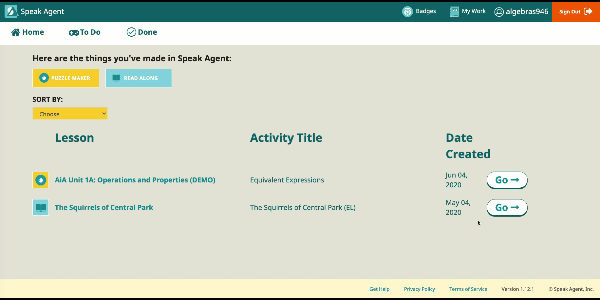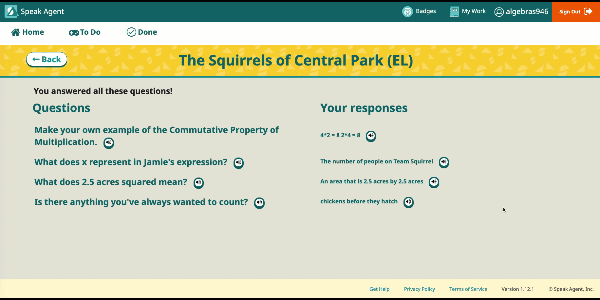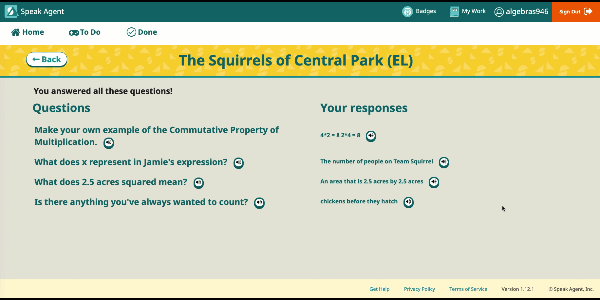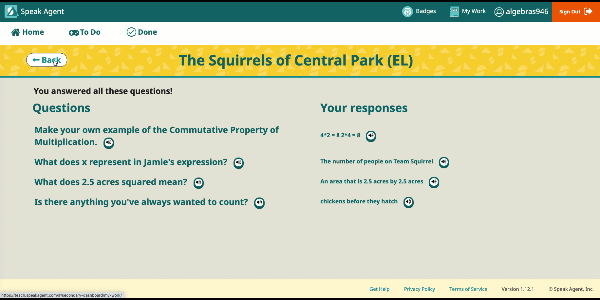
| Unit 01A: Operations and Properties | Ways to write whole numbers and operations. Applying the order of operations. Equivalence of numerical expressions. Properties of operations. | HSA.APR.A.1 |
| Unit 01B: Interpreting and Evaluating Expressions | Properties of operations. The distributive property. Constants, coefficients, and variables. Equivalent expressions. Interpreting expressions. Evaluating expressions. | HSA.SSE.B.4, HSA.SSE.A.1.A, HSA.SSE.A.1.B |
| Unit 01C: Translating English to Algebra | Translate verbal expressions into algebraic expressions. Translate algebraic expressions into verbal expressions. | HSA.SSE.A.2 |
| Unit 2: Functions | ||
| Unit 02A: Defining and Evaluating Functions | Evaluate functions written in function notation. Analyze graphs to identify function characteristics. Explore relationships between variables. Analyze graphs to quantify relationships. | HSA.SSE.B.3.A, HSA.SSE.B.3.B, HSA.SSE.B.3.C |
| Unit 02B: Graphing Linear Functions | Use ordered pairs to locate points and organize data. Analyze ordered pairs, tables, and graphs to determine if relations are functions. | HSA.REI.D.12 |
| Unit 3: Solving Equations and Inequalities | ||
| Unit 03A: Equations and Inequalities | Create equations with one variable to model problems. Understand how inequalities with one variable can be represented on a number line. Explain the steps to solving an equation and an inequality. | HSA.CED.A.1, HSA.CED.A.3, HSA.REI.B.3, HSA.REI.D.12 |
| Unit 03B: Solving Equations and Inequalities | Use inverse operations to solve one- and two-step linear equations and inequalities. Solve linear equations with decimals and fractions. Use the distributive property to solve equations with a variable. Combine like terms. Solve equations with variables on both sides. | HSA.REI.B.3 |
| Unit 03C: Linear Systems | Determine whether an equation has one solution, no solution, or infinitely many solutions. Explain steps to solve an equation or inequality. | HSA.REI.C.6, HSA.REI.C.7, HSA.REI.C.8, HSA.REI.D.12 |
| Unit 4: Linear Functions and Equations | ||
| Unit 04A: Linear Functions | Find the intercepts on graphs of linear equations. Interact with equations in slope-intercept form. | HSA.REI.B.3, HSA.REI.C.6, HSA.REI.C.7, HSA.REI.C.8, HSA.REI.C.9, HSA.CED.A.1, HSA.REI.D.11 |
| Unit 04B: Linear Equations | Use the slope formula for rates of change. Interact with equations in slope-intercept form. Create equations that model linear relationships between two quantities. Determine if lines are parallel, perpendicular, or intersecting. | HSA.REI.B.3, HSA.REI.C.6, HSA.REI.C.7, HSA.REI.C.8, HSA.REI.C.9 |
| Unit 04C: Correlations | Work with scatter plots. Understand the process of determining the line of best fit and how it may apply to real-life situations. | HSS.ID.C.9 |
| Unit 04D: Point-Slope Form | Use x- and y-intercepts to graph equations in standard form. Use the slope and a point of a line to write and graph equations in point-slope form. | 8.EE.B.5, 8.EE.B.6, 8.F.A.3 |
| Unit 5: Data Analysis | ||
| Unit 05A: Measures of Central Tendency | * Find the mean, median, and mode. * Use measures of central tendency to analyze data. | HSS.ID.A.2 |
| Unit 05B: Representing Data | * Use box-and-whisker plots. * Use stem-and-leaf plots. * Use line and dot plots. * Understand how each type of plotting can be used to analyze data and make informed decisions. | HSS.ID.A.3 |
Geometry
Speak Agent Geometry+Language℠ helps students to master key Geometry concepts and to develop critical skills such as math communication, reasoning, and problem-solving. How? By seamlessly integrating academic language activities such as listening and speaking, real-world math stories, reading and writing scaffolds, crafting explanations, and tools for students to create and share their own math problems. Speak Agent maps to your existing curriculum.
| Unit | Common Core State Standards |
|---|---|
| Construction & Rigid Transformations | G.CO.1, G.CO.2, G.CO.3, G.CO.4, G.CO.5 |
| Congruence | G.CO.6, G.CO.7, G.CO.8, G.SRT.5 |
| Parallel Line Angle Relationships | G.CO.9, G.CO.10, G.CO.11 |
| Introduction to Geometry and Constructions | G.CO.12, G.CO.13 |
| Similarity | G.SRT.1a, G.SRT.1b, G.SRT.2, G.SRT.3, G.SRT.4 |
| Right Triangles and Trigonometry | G.SRT.6, G.SRT.7, G.SRT.5, G.SRT.8 |
| Composing and Decomposing Shapes | G.C.1, G.C.2, G.C.3, G.C.5 |
| Coordinate Geometry | G.GPE.4, G.GPE.5, G.GPE.6, G.GPE.7 |
| Equations of Circles | G.GPE.1 |
| Solid Geometry | G.GMD.1, G.GMD.3 |
| Conic Sections | G.GMD.4 |
Geometry Foundations (ELD course)
| Unit | Common Core State Standards |
|---|---|
| Scale and Proportional Relationships | 7.RP.A.2.a, 7.RP.A.2.b |
| Defining and Evaluating Functions | 8.F.1 |
| Basic Characteristics of Functions | 8.F.2, 8.F.3 |
| Graphing Linear Functions | 8.EE.5, 8.EE.6 |
| Other Representations of Linear Functions | 8.F.4, 8.F.5 |
| Equivalent Expressions | 7.EE.1, 7.EE.2 |
| Multi-Step Equations | 7.EE.3, 7.EE.4 |
| Inequalities | 7.EE.4 |
| Solving Linear Equations | 8.EE.7 |
| Solutions of Linear Systems | 8.EE.8 |
| Bivariate Data | 8.SP.1, 8.SP.2 |
| 2D Shapes and Area | 6.G.1 |
| 3D Shapes and Volume | 6.G.2 |
| Coordinate Planes | 6.G.3 |
| Ratios | 7.RP.1 |
| Scale Drawings | 7.G.1 |
| Proportional Relationships | 7.RP.2a, 7.RP.2b, 7.RP.2c, 7.RP.2d |
| Transformations | 8.G.1, 8.G.2, 8.G.3, 8.G.4 |
Other Courses
- CCSS Integrated Math 1
- CCSS Integrated Math 2
The Learning Progression
Every Math+Language lesson for high school courses has three phases:
- We begin by introducing the key mathematical concepts. Students engage in listening, speaking, reading, and morphology practice using visual aids.
- Next, we build background knowledge and connect your curriculum content to the real world. Students engage in reading and interacting with simplified but age-appropriate texts.
- In the third phase, students build content knowledge by communicating their reasoning. At this phase we ramp up the text complexity and add opportunities for open-ended expression and math modeling.
When do you use a lesson?
Each digital lesson spirals in a three-step learning progression:
- Before Each Unit: Provides visual aids to introduce key concepts and foundational vocabulary. Engages students in listening, speaking, and morphology practice.
- At the Start of Each Unit: Uses simplified but age-appropriate interactive stories, texts, and videos to build background knowledge and make connections to the real world.
- During Each Unit: Engages learners using reading and writing activities with leveled, accessible texts to deepen content knowledge and have students demonstrate their reasoning and communication skills.
Activities and Features
Meet with us about math!
Discover how we can address your unique math lesson needs and priorities!